Connection Proxies
The Connection Proxy component is the gateway between users and resources they want to access that utilize RDP, SSH or traditional VNC. Container based desktops and apps do not utilize the Connection Proxy component. The proxy role is comprised of 3 different containers, which have different responsibilities. Connection proxies are automatically registered with the Kasm deployment when installing the Connection Proxy component on a server. For Kubernetes deployments, Kasm will always show a single instance of each component type.
Connection Proxies
Components
Guacamole (GUAC)
Kasm utilizes a custom compiled build of Apache guacd in combination with our own micro service for controlling guacd. Guacd is used for web-native connections to backend RDP, VNC, and SSH servers. Kasm spawns 1 guacd service per core on the system and automatically load distributes sessions between the services, providing for better use of system resources on multi-core systems. Administrators can override this default of 1 guacd service per core by using the --guac-cluster-size N flag on installation, where N signifies the number of guacd instances you wish to be running on the system.
RDP Gateway
The RDP gateway is a set of additional functionality that was added to the Connection Proxy role in Kasm Workspaces 1.16.0. It provides a proxy capability allowing users to connect to Kasm Windows workspaces utilizing their client’s RDP thick client. This allows several features that are not possible with Kasm’s web native RDP access method. Namely smart card, USB, and webcam passthrough from the user’s client machine into the Kasm session while maintaining Kasm’s DLP protections.
This is supported with Windows, Linux, ChromeOS and macOS clients though the instructions to get a seamless experience differ for each OS see Auto-Opening RDP Files for more details.
Users/Administrators can utilize whichever RDP connection software that is required by company policy or personal preference. Kasm Technologies has tested the Microsoft client on Windows and macOS and the XtraLogic client on ChromeOS. The client chosen must support the desired features for instance not all clients support smart card passthrough.
RDP HTTPS Gateway
The RDP HTTPS Gateway allows for RDP connections to traverse over HTTPS, primarily used to facilitate connections through enterprise security firewalls and other security devices. The RDP HTTPS Gateway follows the Microsoft Remote Desktop Gateway Server Protocol. The Kasm RDP HTTPS Gateway does not understand the RDP protocol itself, but rather tunnels the underlying RDP protocol through web based transport. Because this component does not understand RDP, it is used in conjunction with the RDP Gateway covered in the above section.
RDP Native Connections
By default, when a client connects to a Kasm session with an RDP client, it will come first to the RDP HTTPS Gateway, then to the RDP Gateway, and finally to the destination server. Administrators can disable the RDP Gateway or the RDP HTTPS Gateway to reduce overhead, however, there are consequences for disabling either. Disabling the RDP HTTPS Gateway will mean clients will connect to Kasm using the RDP protocol, which may not be allowed through some firewalls that are not in your control. If this is not an issue in your environment, or the environments where clients will connect from, then this may be a good way of increasing the performance of the connection proxy server and thus improving user experience. Admins can uncheck the Enable RDP HTTPS Gateway setting in Zone Settings to achieve this.
Conversely, the RDP Gateway can be disabled by the administrator by unchecking the Enable RDP HTTPS Gateway DLP option in the Zone Settings. RDP traffic will then directly flow from the RDP HTTPS Gateway to the destination server, without traversing the RDP Gateway component which facilitates DLP and SSO features. Disabling the RDP Gateway can significantly reduce bandwidth consumption and improve end-user experience with the following drawbacks:
Data Loss Prevention controls will not be enforced by Kasm. These include settings such as allowing clipboard, uploads, and downloads. Many of these settings can also be enforced through Windows Group Policy.
SSO is only supported when the RDP traffic goes through the RDP Gateway. Without the RDP Gateway users will get prompted to input credentials. Smartcard authentication into Windows will continue to work with the RDP HTTPS Gateway DLP disabled.
Static credentials assigned to a server in Kasm are not passed through in RDP sessions when the RDP Gateway is disabled.
Microsoft RemoteApp support with the RDP Gateway disabled is not a supported configuration.
Architecture
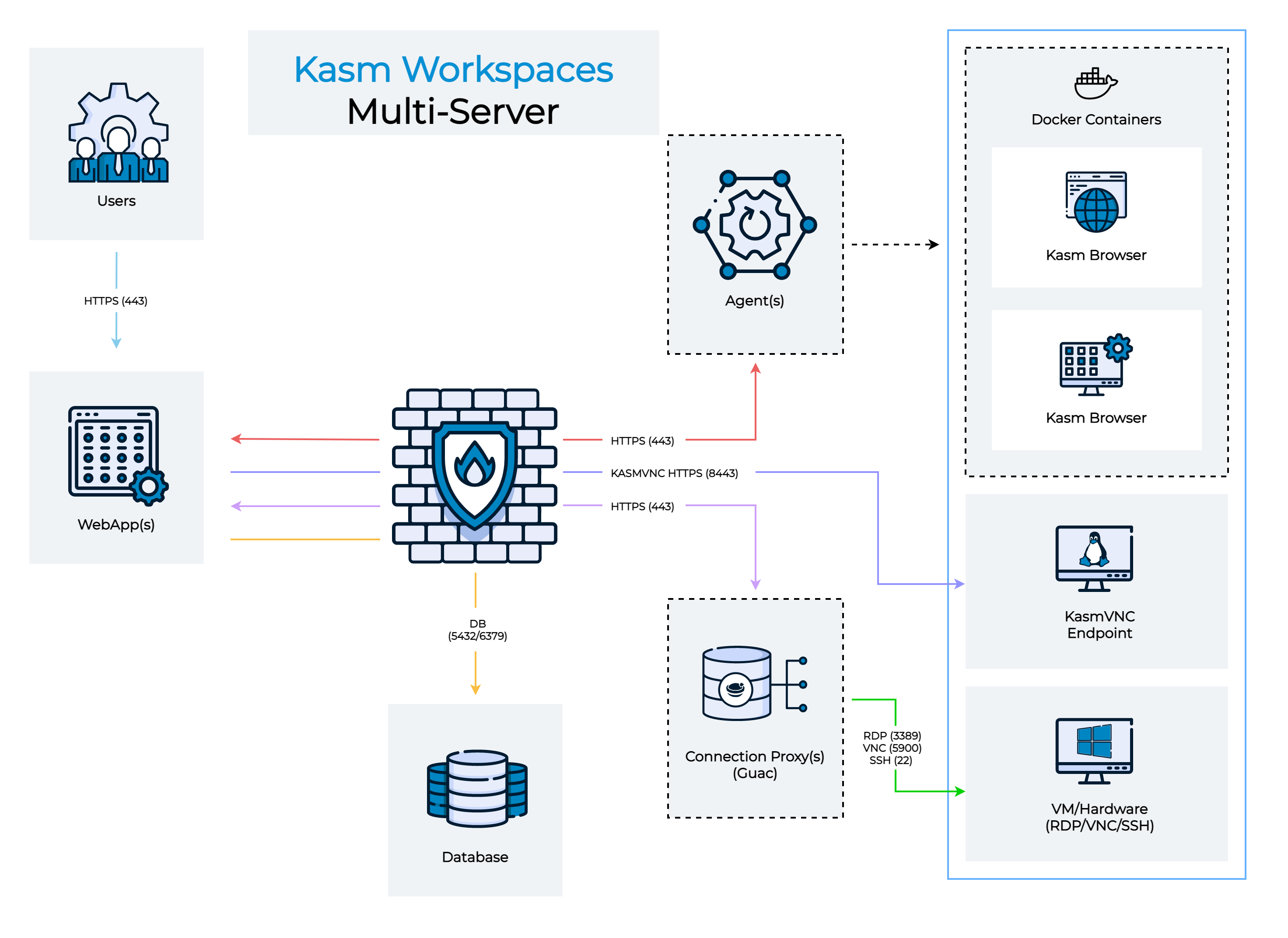
Architecture
The above diagram shows the architecture and user flow of traffic. For Kasm guac sessions, when a user connection to a remote session comes in, shown in light blue, the request can optionally be load balanced between multiple web app servers. The Web App server queries the database for a list of potential connection proxy servers that are responsible for the Kasm Deployment Zone that the requested server is in. The Web App service goes down the list of connection proxies in random order and performs a health check. The user’s HTTPS connection is then proxied to the first connection proxy server (light purple line), in the request zone, that succeeds the health check. This sequence of events ensures resiliency in the event of networking or server issues with a single connection proxy. For Kasm RDP gateway sessions, when a user connection to a remote session comes in, shown in light blue, the request can optionally be load balanced between multiple web app servers. The Web App server queries the database for a list of potential RDP gateway connection proxy servers that are responsible for the Kasm Deployment Zone that the requested server is in. The Web App service goes down the list of RDP gateway connection proxies in random order and performs a health check. When a healthy server is found the Web App server builds an RDP file targeting the selected RDP gateway server and presents it to the user’s browser for download. The user’s RDP client then makes a connection over HTTPS(443) or 3389, depending on if the RDP HTTPS Gateway is enabled, to the Kasm RDP gateway service (dark blue line), which is then proxied to the RDP target. This sequence of events ensures resiliency in the event of networking or server issues with a single RDP gateway connection proxy.
When the connection from the user enters either the RDP gateway or guac connection proxy, it performs an authentication request up to the Web App Role server (light purple line) to authenticate the user, authorize that the user has access to the requested server, and to download connection details for the server. The connection proxy then performs an RDP connection to the remove server (green line).
Single server deployments have all roles installed on a single server. For multi-server deployments, you should consider deploying at least 2 connection proxy servers per Kasm deployment zone. Kasm will automatically load balance users and provide automatic fail-over should one stop responding.