Deployment Zones
Deployment Zones are created to enable logical grouping of Kasm services. In large or distributed deployments, it may be desirable to route users to Kasm services that are closer geographically to improve the user experience. In other use cases, Deployment Zones might be defined for special network segments representing different tenants or security enclaves. Administrators can then leverage standard routing, DNS, load balancing, or other networking techniques to direct user traffic to a desired Zone.
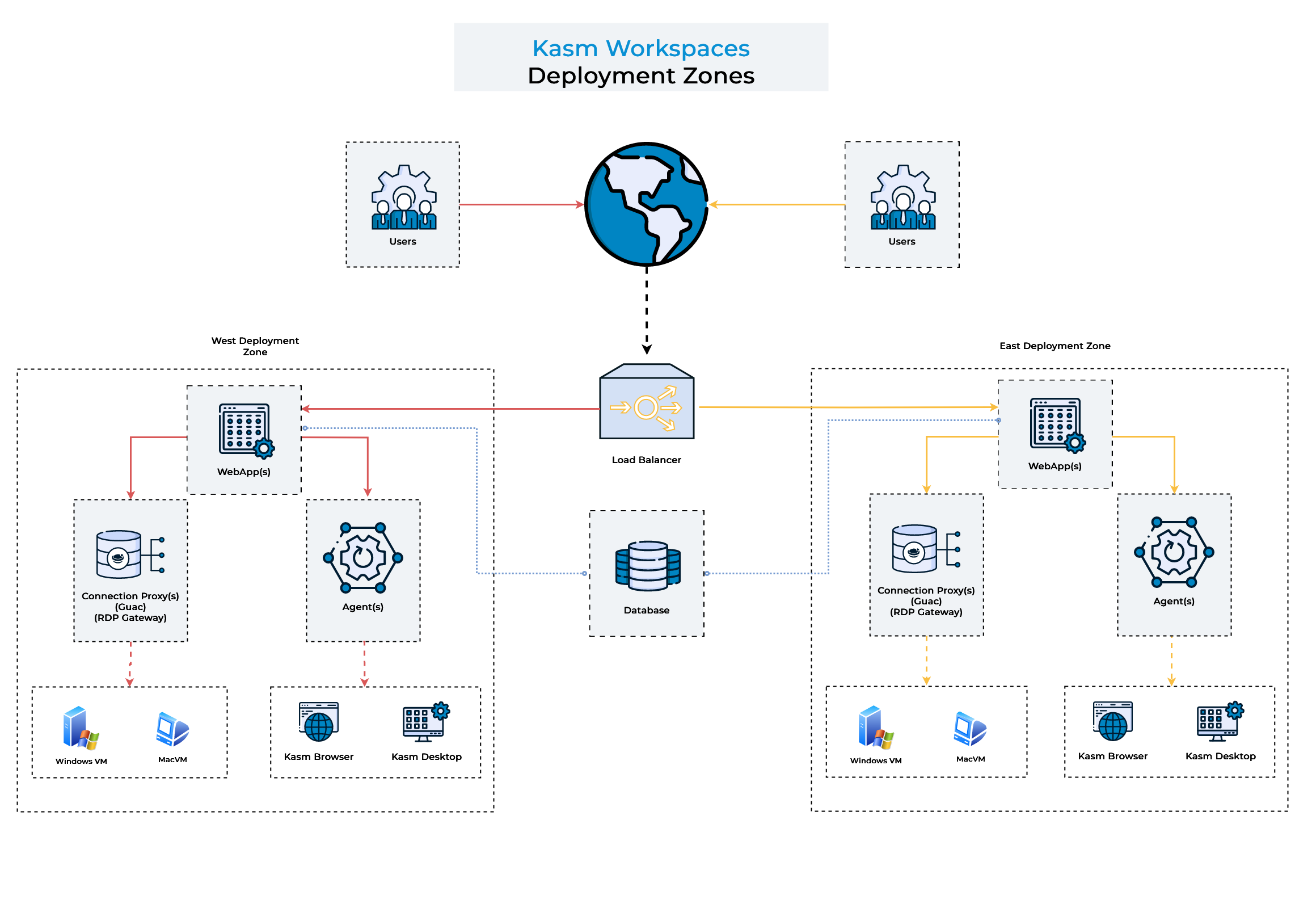
Deployment Zones Diagram
Capabilities
Utilizing multiple deployment zones allows administrators to:
Prefer end-user sessions are provisioned in the Deployment Zone the user is connected to.
When a user connects to the Kasm UI, the server will attempt to provision the Kasm on Agents in the same Zone, only falling back to other Agent’s in other Zone’s if all Agents in the current zone are full or unavailable.
Restrict certain Workspaces to only provision on Agent’s within a given Deployment Zone. See Add/Edit Kasm Workspace
This option is most useful if the Deployment Zones represent special network enclaves that only certain Workspaces and perhaps certain Users should be allowed to access.
Configuring Deployment Zones
Defining Zone Configurations
Existing Deployment Zones can be updated in the UI by an administrator.
Note
Deployment Zones can only be created at Web App installation time. See the instructions for more information.
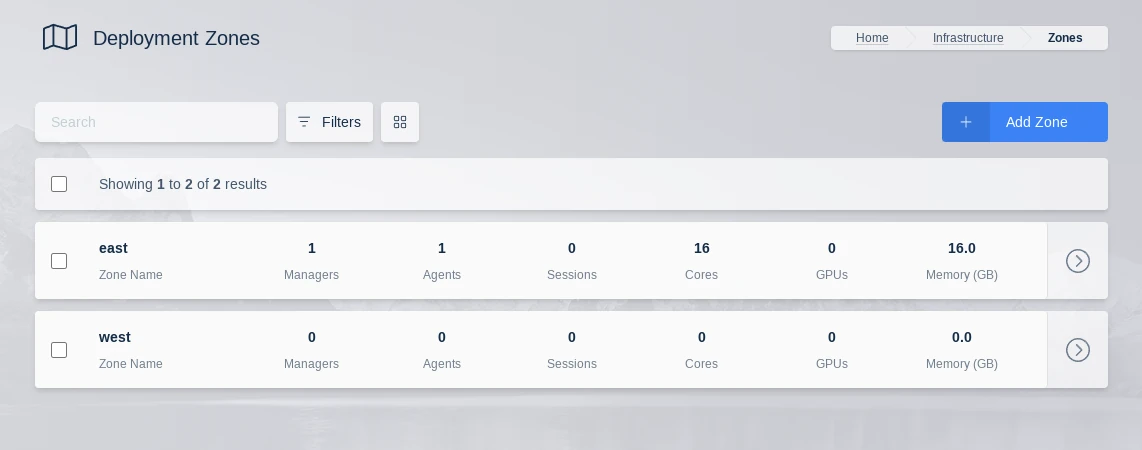
Zones List
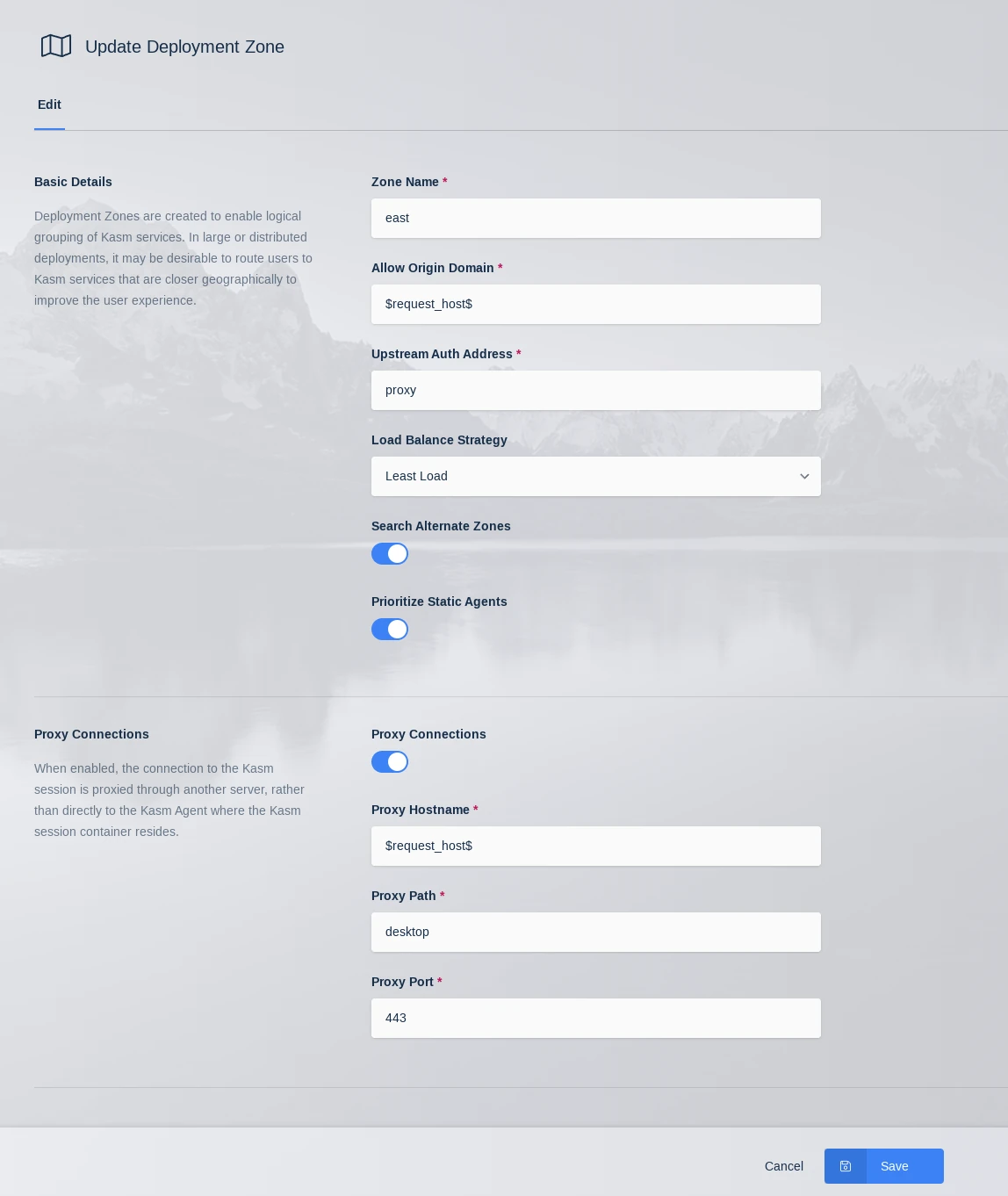
Update Zone
Field |
Description |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|
Zone Name |
The Name given to the Zone |
|
Allow Origin Domain |
Connections to Kasm sessions are restricted to authorized Origins. This value is the authorized origin domain. |
“$request_host$” |
Upstream Auth Address |
Connections to Kasm session are authenticated against a Kasm API server. This value is the address of the server. |
“proxy” |
Load Balance Strategy |
When a user requests a new Kasm session, the server can use several Load Balance Strategies to determine which Agent(s) to prioritize for the request.
*For Server Pools of type Server, load is estimated by comparing the number of current Kasm sessions to the configured supportable number of sessions. |
Least Load |
Search Alternate Zones |
When a user requests a Kasm, the initial Zone considered for session resources is the Zone specified by the user, or the Zone determined to be closest to the user if the former is not specified. By default, that is the only Zone that will be considered for session creation. Enabling this setting allows other Zones to be searched for resources if this Zone is the initial Zone and it cannot host the requested Kasm. |
Enabled |
Prioritize Static Agents |
Utilize fixed agents before using auto scaled Docker Agents. |
Enabled |
Proxy Connections |
When disabled, the user will make a connection to Kasm session directly to the Kasm Agent where the Kasm session container resides. When enabled, the connection to the Kasm session is proxied through another server |
Enabled |
Proxy Hostname |
The location of the proxy server when Proxy Connections is enabled. |
“$request_host$” |
Proxy Path |
The base path to append to the Kasm connection when Proxy Connections is enabled. |
“/desktop” |
Proxy Port |
The port to use for the proxy server when Proxy Connections is enabled. Kasm Workspaces will attempt to automatically determine the correct port from window.location.port |
“0” |
Proxy RDP Local Client Connections |
When enabled, RDP connections made from native RDP clients are proxied through one or more Kasm Web App servers, to the Kasm RDP Gateway. This allows all requests to come through a single domain name. When disabled, RDP clients will connect directly to the Kasm RDP Gateway component, which is part of the Guac role. This requires the Guac role servers to have a public IP address and resolvable hostname. This setting applies only when the zone setting Enable RDP HTTPS Gateway is enabled. |
Enabled |
RDP HTTPS Proxy Hostname |
The hostname/ip of a load balancer or proxy in front of the HTTPS based RDP Gateway component. |
“$request_host$” |
RDP HTTPS Proxy Port |
The port number of a load balancer or proxy in front of the HTTPS based RDP Gateway component. |
“443” |
Restrict RDP Client IP Address |
Require that the client’s IP address be the same on the incoming RDP connection as on the API call that requested the session from the Kasm dashboard. In general, this restriction is not compatible in situations where the client IP address may change inbetween requests to Kasm such as load balances, reverse proxies or cloudflare tunnels. |
Disabled |
Enable RDP HTTPS Gateway |
Use the HTTPS RDP Gateway protocol. When disabled, standard RDP over port 3389 is used. |
Diabled |
Enable RDP HTTPS Gateway DLP |
Send HTTPS RDP connections through DLP (Data Loss Prevention). Enabling DLP has performance and scalability implications. Disabling DLP will disable many data loss prevention features enforced by Kasm, however, many of these features can be enforced by proper Group Policy in Windows. Disabling DLP will also break single sign on. This setting applies only when the zone setting Enable RDP HTTPS Gateway is enabled. |
Disabled |
Note
$request_host$ referenced as the default for several settings above can be used to automatically reference the domain/host used in the URL to access the Kasm deployment.
For example if users accesses Kasm via https://east.kasm.server , $request_host$ will be east.kasm.server.
Assigning Zone Configurations
Agents are assigned the Zone of whichever manager they are currently checked in to.
Once defined, the Kasm services need to be configured to be members of the given Zone. The Deployment Zone setting for API Servers (kasm_api, kasm_manager) is set their configuration file. The default zone is default
grep zone_name /opt/kasm/current/conf/app/api/api.app.config.yaml
zone_name: east
Ensure all Kasm services are stopped
sudo /opt/kasm/bin/stop
Edit the zone_name property in api.app.config.yaml
vi /opt/kasm/current/conf/app/api/api.app.config.yaml
Restart the Kasm Services
sudo /opt/kasm/bin/start